
The Role of Nutrition in Pain Management
In recent years, the importance of nutrition in pain management has gained significant attention. "Role of Nutrition in Pain Management": A healthy dietary habit or proper nutrition plays a crucial role in relieving chronic pain, preventing its onset, and improving the overall quality of life for those suffering from various pain conditions.
In this blog, we will explore the relationship between nutrition and pain, the role of specific nutrients in pain management, and how to incorporate a balanced diet into your pain management plan.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Chronic pain, a pervasive and complex health issue, often finds its roots in inflammation. Inflammatory responses, designed to protect the body, can become chronic, contributing to sustained pain. Understanding this link is crucial for effective pain management.
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or illness. However, when this response becomes chronic, it can lead to persistent pain. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia often involve heightened levels of inflammation, exacerbating discomfort.

The Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet in Managing Chronic Pain
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet emerges as a promising strategy for managing chronic pain. Certain foods possess anti-inflammatory properties, helping to mitigate the systemic inflammation associated with various pain conditions. Below are some of the foods to eat:
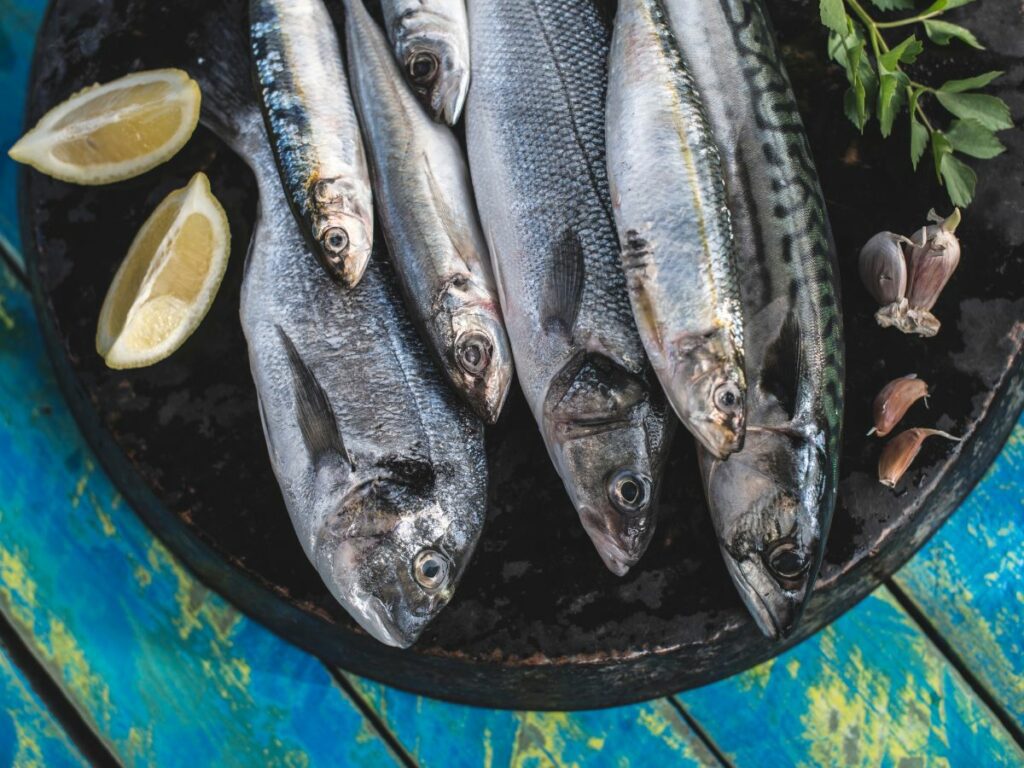
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these can reduce inflammation.
- Colorful Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants, they combat inflammation. Berries, kale, and broccoli are excellent choices.
- Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, ginger, and garlic have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3s known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens offer a variety of vitamins and minerals.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseeds, and chia seeds provide healthy fats and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Weight Management and Pain
Weight plays a pivotal role in the experience and management of chronic pain. Excess weight can contribute to the development or exacerbation of conditions such as osteoarthritis, back pain, and joint discomfort. Understanding the interplay between weight and pain is essential for comprehensive well-being.
Excessive weight places additional stress on joints, particularly in weight-bearing areas such as the knees and hips. This stress can accelerate the degeneration of cartilage, leading to increased pain and reduced mobility.
Focus on Maintaining a Healthy Weight Through Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy weight is a multifaceted endeavor that involves both dietary choices and regular physical activity. The symbiotic relationship between diet and exercise is crucial for sustainable weight management and pain reduction. Below are some coping strategies:
- Regular Exercise: Incorporate both aerobic and strength-training exercises to support weight loss and enhance overall well-being.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, fostering a healthy relationship with food.
- Professional Guidance: Consult with healthcare professionals or nutritionists for personalized weight management plans.
Chronic Pain Conditions Related to Poor Nutrition
Understanding the intricate connection between nutrition and chronic pain conditions provides valuable insights into adopting a holistic approach to pain management. By making informed dietary choices, individuals can complement traditional treatments and potentially reduce the severity of symptoms.

Spine Spondylosis or Early Degenerative Disc Disease
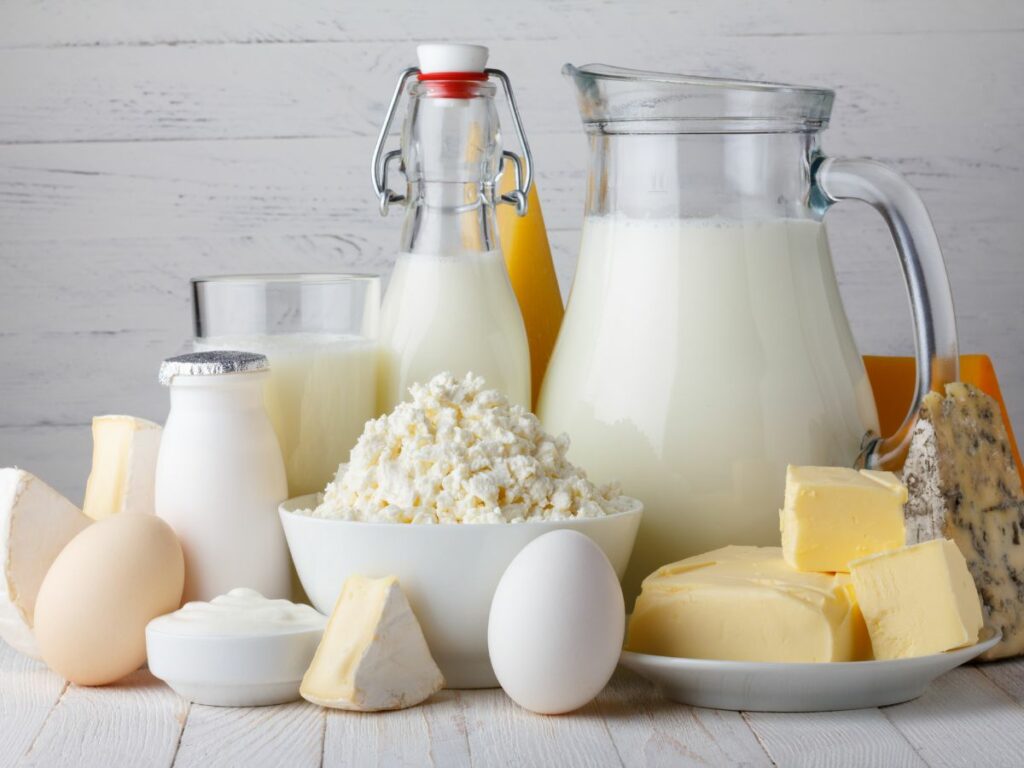
Chronic back pain, commonly associated with spine spondylosis or early degenerative disc disease, can be exacerbated by poor nutrition. A diet lacking essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D may contribute to the weakening of spinal discs, intensifying pain.
Incorporating foods rich in these nutrients, such as dairy products and leafy greens, can support spine health and alleviate discomfort.
Knee Joint Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis in the knee joints is a prevalent condition, and poor nutrition can exacerbate inflammation and joint degradation. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, including omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and nuts, can aid in managing knee osteoarthritis.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition is crucial for reducing stress on the knee joints.
Osteoporosis
Poor nutrition can contribute to the development of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones and increased susceptibility to fractures.
Adequate calcium and vitamin K intake are vital for bone health. Dairy products, green leafy vegetables, and fortified foods can provide these essential nutrients, helping prevent and manage osteoporosis-related pain.
Slip Disc
The condition of a slipped disc can be worsened by inflammation, which is influenced by dietary choices. Anti-inflammatory foods, such as berries and turmeric, can be beneficial in managing pain associated with a slipped disc. Additionally, maintaining a diet that supports spinal health is crucial for preventing further complications.
Other Joint Arthritis
Various forms of arthritis affecting different joints can be exacerbated by poor nutrition. Ensuring an adequate intake of antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables can help manage inflammation associated with arthritis. Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin C are also essential for joint health, providing a natural approach to pain management.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a complex condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain. Nutritional choices can influence the severity of symptoms. A balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, and a variety of fruits and vegetables can contribute to overall well-being and potentially alleviate fibromyalgia-related pain.
Nerve Pain or Neuropathic Pain
Nerve pain can be influenced by nutritional deficiencies, particularly in B vitamins. Incorporating foods rich in B vitamins, such as leafy greens, legumes, and nuts, can support nerve health and mitigate neuropathic pain.
Musculoskeletal Pain
Musculoskeletal pain, affecting muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and other elements of the musculoskeletal system, can be linked to nutritional imbalances. Maintaining a diet that supports muscle function and repair, including an adequate protein intake, is essential for managing musculoskeletal pain.
Migraine Headache
Migraine headaches can be triggered or intensified by certain foods. Identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as caffeine and certain additives, can play a crucial role in migraine management. Additionally, staying hydrated and maintaining stable blood sugar levels through a balanced diet can contribute to headache prevention.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis involves chronic inflammation, and nutrition plays a vital role in modulating the inflammatory response.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Moreover, maintaining a diet that supports a healthy gut microbiome may also contribute to managing symptoms.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, characterized by pain and numbness in the hand and arm, can be influenced by factors such as inflammation. Anti-inflammatory foods, coupled with maintaining proper wrist and hand posture, can aid in managing pain associated with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Gout Arthritis
Gout, a form of arthritis, is linked to elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. Dietary choices can significantly impact uric acid levels. Avoiding purine-rich foods, such as red meat and certain seafood, and staying hydrated can help prevent gout attacks and manage pain associated with this condition.
Implementing a Balanced Diet for Pain Management
Ensuring a diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for managing chronic pain effectively. Here, we will explore key dietary components and their impact on pain relief.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Incorporating a variety of anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fatty fish, can help reduce inflammation associated with many chronic pain conditions. These foods contain antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, contributing to a healthier inflammatory response.
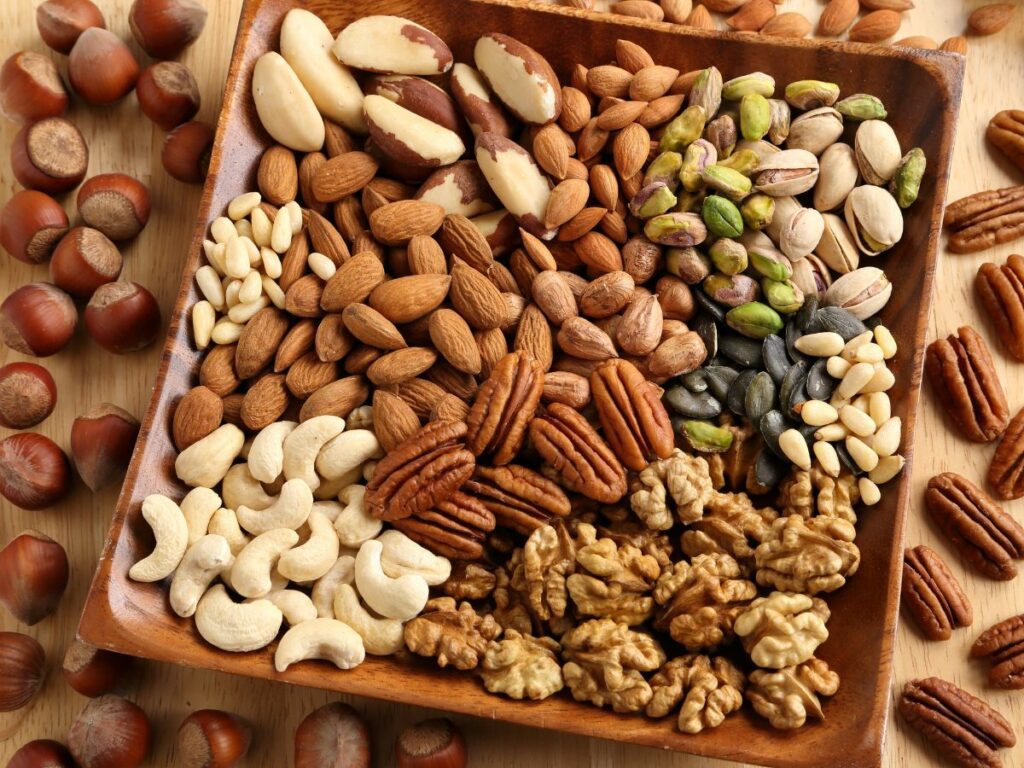




- Nutrients for Bone Health: For conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis, prioritizing nutrients essential for bone health is paramount. Calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin K play crucial roles in maintaining bone density and preventing deterioration. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources of these nutrients.


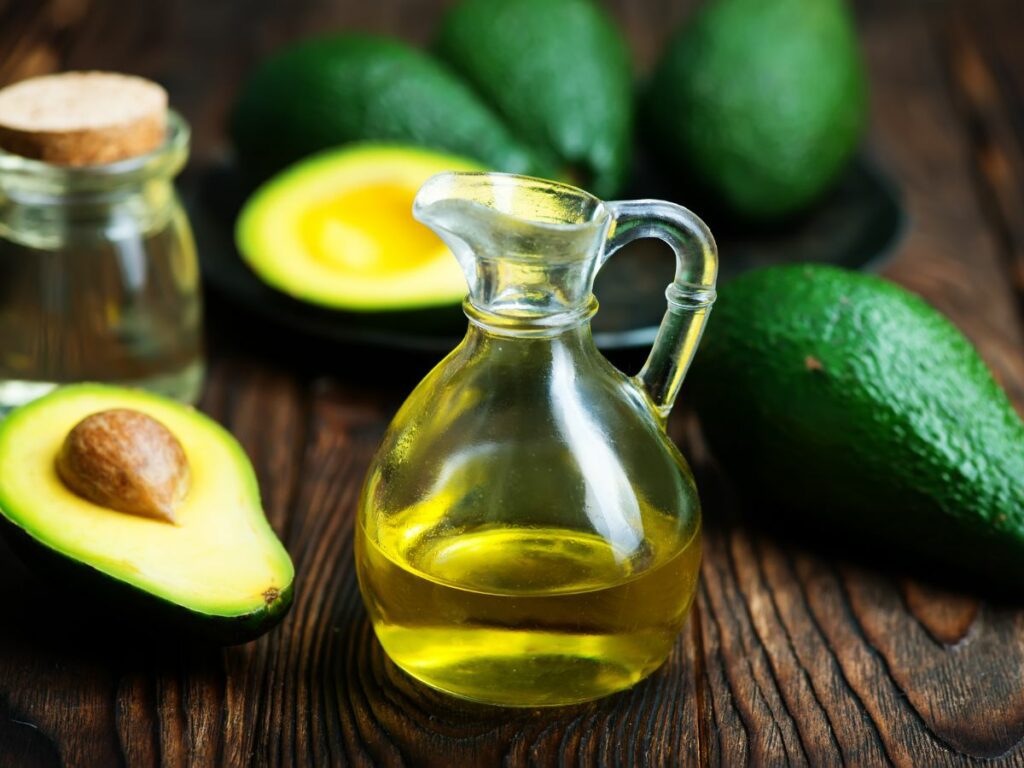
- Balanced Macronutrients: Achieving a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential for overall health and can contribute to pain management. Adequate protein intake supports muscle function and repair, while healthy fats, such as those found in avocados and olive oil, have anti-inflammatory properties.


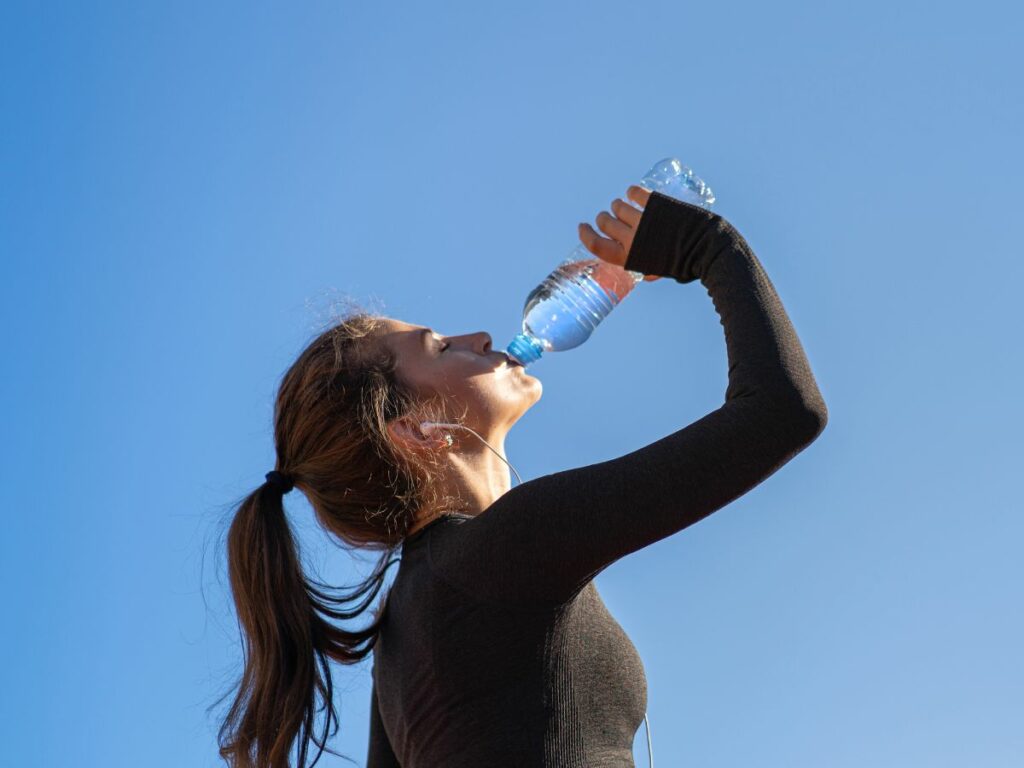
- Hydration (H3): Staying well-hydrated is essential for overall health and can impact conditions like gout and migraines. Proper hydration helps flush out toxins, supports joint lubrication, and can reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.

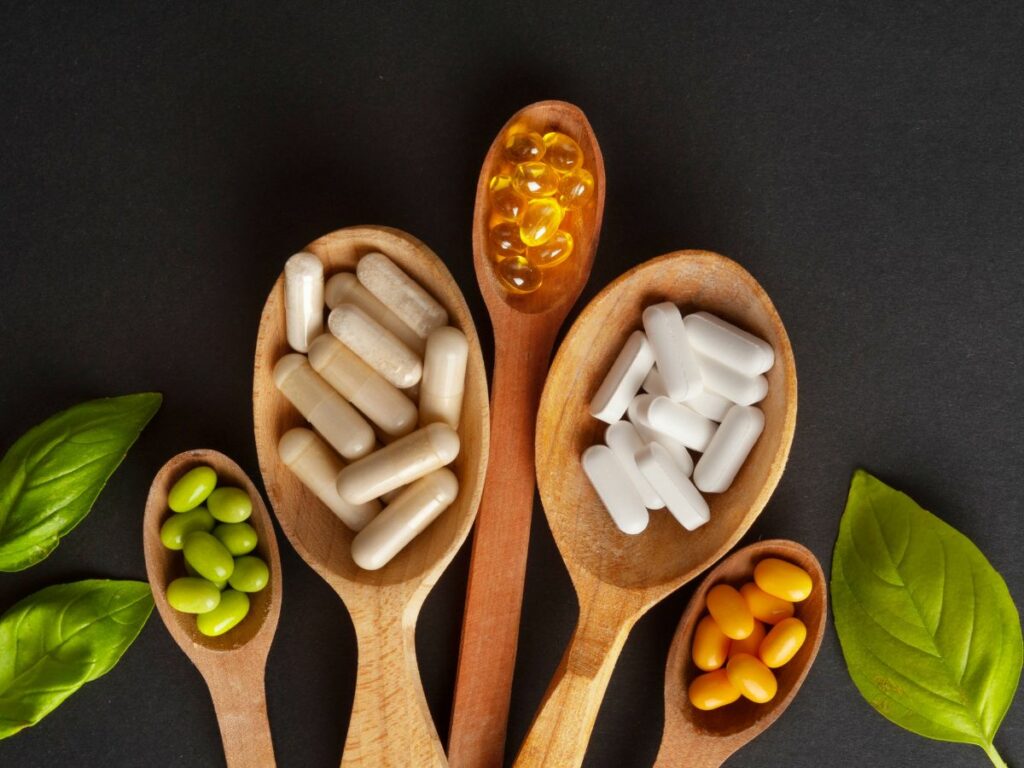
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplementation: In some cases, nutritional deficiencies may require supplementation. Consultation with a healthcare professional can help determine if specific vitamins or minerals need to be supplemented to address pain-related issues.

Lifestyle Changes to Manage and Prevent Nerve Pain
The role of nutrition in pain management, particularly nerve pain, cannot be overstated. A well-balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, essential vitamins, and minerals can significantly alleviate discomfort and promote overall nerve health.
Integrating lifestyle changes that prioritize nutrition, such as reducing processed foods, embracing a plant-based diet, and staying hydrated, becomes paramount in managing and preventing nerve pain.
By fostering a holistic approach to wellness through mindful dietary choices, individuals can proactively address the root causes of pain and embark on a journey toward lasting relief. Remember, the power to soothe nerve pain lies not just in prescriptions but in the plate as well.
About Dr. Sean Ormond



