
How to Manage Pain from Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition caused by the compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. It affects millions of people worldwide, especially those engaged in repetitive hand movements like typing or manual labor.
Proactive management is crucial to prevent permanent nerve damage, which can lead to significant loss of hand function. Early intervention through lifestyle adjustments, stress management, and medical treatment can help mitigate the effects of CTS and preserve quality of life.
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
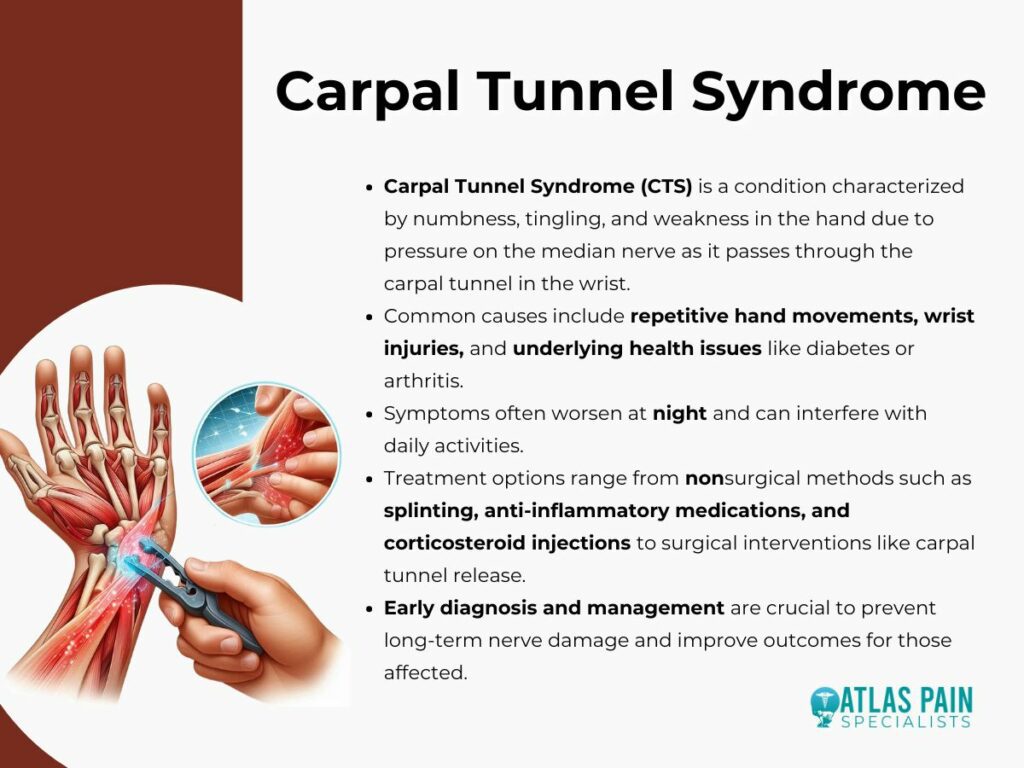
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition caused by the compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. This tunnel is a narrow passageway made of bones and ligaments.
The median nerve controls sensations in the thumb and fingers, except for the pinky, and also aids in hand movements. When the carpal tunnel becomes swollen or narrowed, it puts pressure on this nerve, leading to the characteristic symptoms of CTS.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The most prevalent symptoms of CTS include pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand and fingers, particularly in the thumb, index, and middle fingers. These sensations often worsen at night or after activities that involve repetitive hand movements. Additionally, individuals may experience weakness in their hands, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks, such as gripping objects or typing.
Early diagnosis of CTS is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent long-term damage. If left untreated, CTS can lead to permanent nerve damage and loss of hand function. The diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and may be supported by nerve conduction studies or electromyography to assess the severity of nerve compression. Prompt medical attention can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications, ensuring better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Unique Perspectives on Pain Management
Managing pain, especially from conditions like Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), can benefit from a holistic approach that integrates physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors. This comprehensive strategy not only targets the physical symptoms but also addresses the overall well-being of the individual.
Physical interventions might include exercises to strengthen the wrist and hand muscles, ergonomic adjustments to daily activities, and the use of splints to reduce strain. Emotional factors, such as stress and anxiety, can exacerbate pain, so addressing these through counseling or stress-management techniques is crucial.
Lifestyle changes, such as improving posture, incorporating regular breaks from repetitive tasks, and maintaining a healthy diet, can also play a significant role in alleviating pain and preventing further issues. By considering the interplay of these factors, individuals can achieve a more balanced and effective pain management plan.
Mind-Body Connection
The mind-body connection plays a vital role in how pain is perceived and managed. Techniques such as mindfulness and meditation can be particularly effective in managing pain from CTS.
Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment and acknowledging pain without judgment, which can reduce the emotional impact of pain and improve overall coping strategies.
Meditation, on the other hand, can help relax the body and mind, reducing the stress and tension that often accompany chronic pain. Both practices encourage a shift in perspective, allowing individuals to manage pain more effectively by influencing their emotional and physiological responses.
Incorporating these techniques into a pain management routine can enhance one's ability to handle pain and improve quality of life, offering a valuable complement to traditional medical treatments.
Actionable Strategies for Pain Relief
Creating a wrist-friendly workspace is crucial for managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) pain.
- Start by adjusting the height of your chair and desk so that your forearms are parallel to the floor while typing.
- Use a keyboard with a slight negative tilt and position your mouse close to the keyboard to minimize reaching.
- Wrist rests can provide additional support, but they should only be used during breaks, not while typing.
- Proper posture is essential; ensure your back is straight, shoulders are relaxed, and wrists are in a neutral position, avoiding excessive bending or twisting.
These adjustments can significantly reduce strain on the wrists, helping to alleviate and prevent CTS symptoms.
Exercise and Stretching
Incorporating specific exercises and stretches into your daily routine can provide relief from CTS.
- Nerve-gliding techniques, which involve gentle movements that stretch the median nerve, can help maintain flexibility and reduce compression.
- Wrist flexor and extensor stretches, as well as grip-strengthening exercises, are also beneficial.
It’s important to take regular breaks during repetitive activities, such as typing or using tools, to perform these exercises and reduce muscle fatigue. Moving your hands and wrists frequently throughout the day keeps the nerves and tendons functioning optimally, reducing the risk of exacerbating CTS symptoms.
Alternative Therapies
Several alternative therapies can complement conventional treatments for CTS.
- Acupuncture has been shown to reduce pain and inflammation by stimulating specific points along the body's meridians.
- Massage therapy can relieve tension in the hand and forearm muscles, improving circulation and reducing nerve compression.
- Chiropractic care, particularly adjustments to the wrist and upper spine, may also alleviate symptoms by improving nerve function.
While the effectiveness of these therapies varies, many individuals report significant relief when combined with traditional approaches.
Dietary Considerations
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can play a role in managing CTS symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, along with antioxidants from fruits and vegetables, can help reduce inflammation. Supplements like turmeric and ginger may also offer anti-inflammatory benefits. Staying well-hydrated is crucial, as dehydration can contribute to nerve irritation. A balanced diet, combined with adequate water intake, supports nerve health and can potentially reduce the severity of CTS symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) by addressing the root causes of symptoms and promoting long-term relief. While medical treatments like splints, medications, or even surgery can help, adjusting daily habits and activities can prevent further aggravation and support recovery. These modifications focus on reducing repetitive strain, managing stress, and making conscious choices that promote wrist health.
Activity Modification
Repetitive strain is one of the primary contributors to CTS. Activities that involve frequent bending, gripping, or twisting of the wrist can lead to the compression of the median nerve over time. Identifying these activities, both at work and in daily life, is the first step toward reducing strain.
For example, if typing is a significant part of your day, using an ergonomic keyboard and taking regular breaks to stretch your hands and wrists can reduce tension. Additionally, shifting to hobbies or tasks that require less repetitive wrist motion can help prevent the worsening of symptoms while still allowing you to stay engaged and active.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress not only affects your mental health but also has a direct impact on physical pain. High levels of stress can lead to increased muscle tension, which may exacerbate CTS symptoms.
Incorporating stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help lower stress levels and reduce the perception of pain. These practices promote relaxation and improve circulation, which can be beneficial for nerve health. By managing stress effectively, you create a more conducive environment for healing and reduce the likelihood of symptom flare-ups.
When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing when to seek professional help for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is critical for preventing long-term complications. While mild cases of CTS can often be managed with home remedies and lifestyle changes, there are specific signs that indicate the need for medical intervention. Ignoring these signs can lead to worsening symptoms and permanent damage to the median nerve, which may result in a significant loss of hand function.
Signs that Indicate the Need for Medical Intervention
One of the key indicators that it’s time to seek professional help is the persistence and progression of symptoms.
- Occasional tingling or numbness in the fingers might not be alarming initially, but if these sensations become more frequent or last longer, they require attention.
- If you start experiencing pain that disrupts your sleep, or if you notice weakness in your grip, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider.
These symptoms suggest that the median nerve is under sustained pressure, and without intervention, this pressure can lead to permanent nerve damage.
Conclusion
Managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) requires a multi-faceted approach that combines lifestyle modifications, stress management, and timely medical intervention. Addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of CTS can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent long-term damage.
Taking proactive steps, such as ergonomic adjustments and regular exercises, is essential. However, if symptoms persist, seeking professional help is crucial for personalized treatment strategies. By being attentive to your body's signals and consulting healthcare professionals, you can effectively manage CTS and maintain your hand function and quality of life.
About Dr. Sean Ormond



