
Everything You Need to Know About Fibromyalgia
Is everything you need to know about fibromyalgia in this article? Yes, Fibromyalgia is a complex and often misunderstood chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties. As an estimated 2-8% of the global population is affected by fibromyalgia, it is essential to understand its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of fibromyalgia, equipping you with the knowledge to identify, manage, and seek support for this condition.
Let’s start!
Table of Contents
What is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, tenderness, stiffness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive issues. Often referred to as a "central sensitization syndrome," fibromyalgia involves an increased sensitivity to pain due to changes in how the brain and spinal cord process pain signals. This condition affects more women than men and is more common in middle-aged individuals.
Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by various symptoms that vary from person to person. The most common symptoms associated with fibromyalgia include the following:
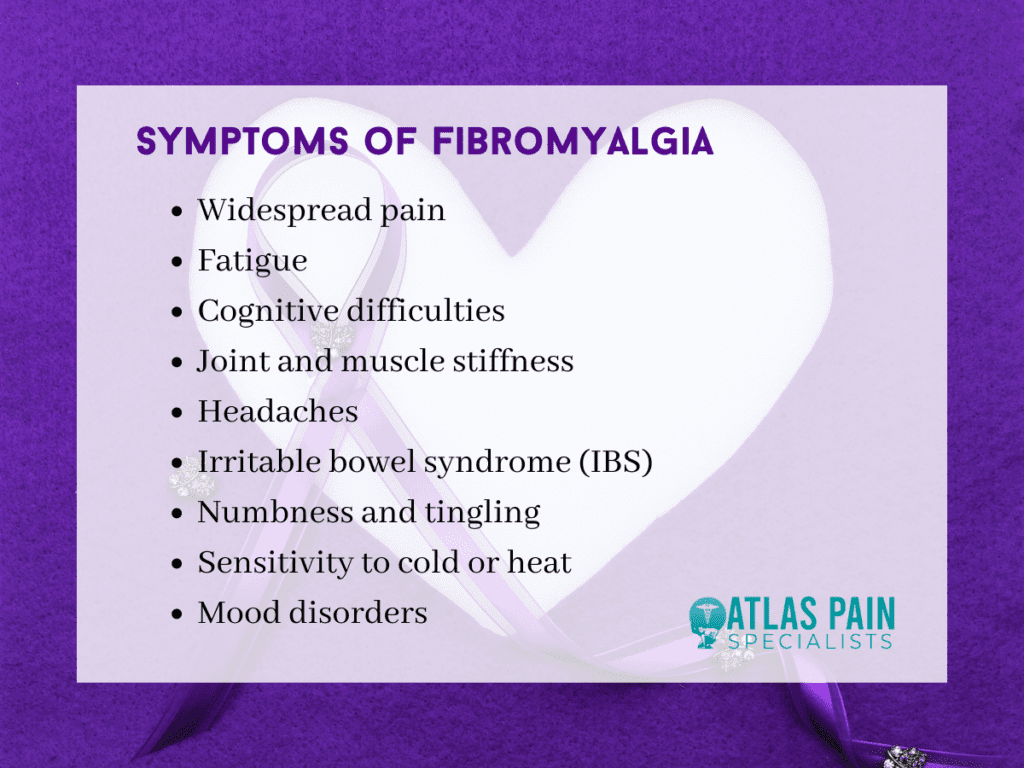
Widespread pain
This is the primary symptom of fibromyalgia, described as a persistent, dull pain lasting at least three months. Why do you feel pain? The pain affects both sides of the body, above and below the waist, and is often accompanied by tenderness in specific areas known as "tender points."
Fatigue
People with fibromyalgia frequently experience persistent fatigue that can be debilitating. They often wake up feeling tired, even after a full night's sleep. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome, can contribute to this exhaustion.
Cognitive difficulties
Often referred to as "fibro fog," cognitive symptoms include problems with memory, concentration, and attention. These issues can make it challenging for individuals with fibromyalgia to perform daily tasks or maintain focus at work or school.
Joint and muscle stiffness
Many people with fibromyalgia experience stiffness in their joints and muscles, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. This stiffness can make it difficult to move or exercise comfortably.
Headaches
Chronic headaches, including migraines, are common among individuals with fibromyalgia. These headaches can be severe and may contribute to the overall discomfort experienced by those with the condition.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
IBS, which causes abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel movements, is frequently experienced by people with fibromyalgia.
Numbness and tingling
Some individuals with fibromyalgia report sensations of numbness or tingling in their hands, feet, arms, or legs. This symptom can be uncomfortable and may interfere with daily activities.
Sensitivity to cold or heat
People with fibromyalgia are often more sensitive to temperature changes, making them more susceptible to discomfort from cold or hot environments.
Mood disorders
Anxiety and depression are common in individuals with fibromyalgia, potentially due to chronic pain, fatigue, and other associated challenges.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency, making it essential for individuals with fibromyalgia to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their specific needs.
Common Causes of Fibromyalgia
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is still unknown, but researchers believe it likely results from genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Some common factors that may contribute to the development of fibromyalgia include:
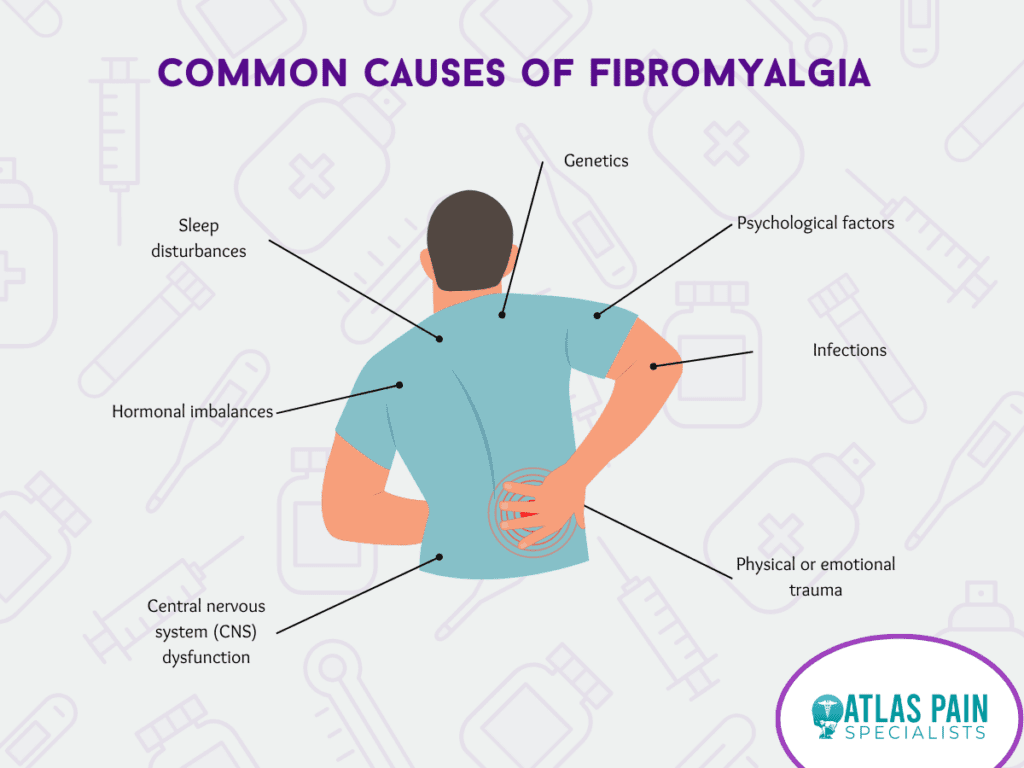
Genetics
Fibromyalgia appears to have a genetic component, as it often runs in families. Individuals with a family history of fibromyalgia may be more susceptible to developing the condition.
Infections
Certain infections, such as viral illnesses or Lyme disease, have been linked to the onset of fibromyalgia. These infections may trigger or exacerbate the condition in some individuals.
Physical or emotional trauma
Traumatic events, such as car accidents or significant emotional stress, can trigger fibromyalgia in some people. This association has led to the hypothesis that fibromyalgia may be related to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction
Research suggests that abnormalities in the way the CNS processes pain signals may contribute to fibromyalgia. This dysfunction, known as central sensitization, increased sensitivity to pain, even in response to normally non-painful stimuli.
Hormonal imbalances
People with fibromyalgia often have lower levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These chemicals play a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, and pain perception. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters may contribute to the development of fibromyalgia symptoms.
Sleep disturbances
Disrupted sleep patterns are common in individuals with fibromyalgia, and poor sleep quality may contribute to the development or exacerbation of the condition. Sleep disturbances can worsen pain and fatigue, creating a cycle perpetuating fibromyalgia symptoms.
Psychological factors
Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression may play a role in developing fibromyalgia. These factors amplify pain perception and contribute to central sensitization, increasing pain sensitivity.
It is important to note that fibromyalgia is a complex and multifactorial condition, and the specific cause or combination of factors may vary from one individual to another. Ongoing research is being conducted to understand the underlying mechanisms of fibromyalgia better and develop more targeted treatments for those affected by the condition.
Treatment of Fibromyalgia
Treating fibromyalgia can be challenging, as there is no one-size-fits-all approach. The primary goal of treatment is to manage symptoms, improve overall functioning, and enhance the quality of life.
A combination of medications, therapy, lifestyle changes, and alternative treatments is often recommended. Here are some common treatment options for fibromyalgia:
Medications:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen sodium may help alleviate mild to moderate pain. Prescription pain relievers may be used in some cases, but their long-term use is generally discouraged due to potential side effects and dependence.
- Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine, and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), like duloxetine and milnacipran, can help alleviate pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances in some individuals with fibromyalgia.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications originally developed to treat epilepsy, such as pregabalin and gabapentin, have been found to be effective in reducing pain and improving sleep in some people with fibromyalgia.
Physical therapy
A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to help improve strength, flexibility, and stamina. Regular exercise has been shown to reduce pain, improve sleep, and enhance overall well-being in individuals with fibromyalgia.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
CBT is a form of talk therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and develop effective coping strategies. CBT is effective in reducing pain, improving mood, and enhancing the overall quality of life in people with fibromyalgia.
Alternative therapies
Some individuals with fibromyalgia may benefit from alternative or complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, yoga, and tai chi. These therapies may help alleviate pain, improve sleep, and reduce stress, although more research is needed to understand their full benefits for fibromyalgia patients.
Lifestyle modifications
- Sleep hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and developing healthy bedtime habits can help improve sleep quality and reduce fatigue.
- Stress management: Learning and practicing stress reduction techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or mindfulness, can help manage stress and alleviate fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular, low-impact physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help reduce pain and improve overall functioning in individuals with fibromyalgia.
- Healthy diet: Consuming a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats may help improve overall health and reduce fibromyalgia symptoms.
Individuals with fibromyalgia must work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive and personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and symptoms. This often requires a combination of treatments and ongoing adjustments to find the most effective approach.
Other Tips For Managing and Coping with Fibromyalgia
Managing and coping with fibromyalgia can be challenging, but implementing various strategies can help improve your quality of life. Here are some tips to help manage and cope with fibromyalgia:

- Build a support network: Surround yourself with understanding family members, friends, and healthcare providers who can provide emotional and practical support. Joining a fibromyalgia support group, in-person or online, can also help you share experiences and coping strategies with others who understand your challenges.
- Develop self-management strategies: Learn and practice self-management techniques to control your symptoms better. These may include relaxation techniques, stress reduction methods, pacing yourself throughout the day, and setting realistic goals for daily activities.
- Educate yourself about fibromyalgia: Understanding your condition can help you make informed decisions about your care and empower you to advocate for yourself. Stay up-to-date on the latest fibromyalgia research, treatments, and coping strategies.
- Communicate with healthcare providers: Maintain open and honest communication with your healthcare team to ensure you receive appropriate care and support. Discuss your symptoms, concerns, and treatment goals, and work together to develop an effective treatment plan.
- Seek professional help for mood disorders: If you're experiencing symptoms of depression or anxiety, consult with a mental health professional. They can help you develop coping strategies and, if needed, recommend an appropriate medication to manage your mood.
- Be patient and kind to yourself: Living with fibromyalgia can be challenging, but it's essential to remember that it's not your fault. Be patient with yourself and acknowledge your progress, even if it's slow. Celebrate your accomplishments, and don't be too hard on yourself when you have difficult days.
Conclusion
Fibromyalgia is a complex and chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Although the exact cause remains unclear, various factors may contribute to its development, including genetics, infections, trauma, and central nervous system dysfunction.
Fibromyalgia presents a wide range of symptoms, making it essential for individuals and healthcare providers to work together to develop a comprehensive and personalized treatment plan. Managing and coping with fibromyalgia can be challenging, but by implementing the various strategies above, individuals living with this condition can improve their overall quality of life.
About Dr. Sean Ormond



