Could What You're Eating Cause Your Foot Pain?
Foot pain is a common complaint among people of all ages, and it can result from various factors such as injury, poor footwear, or underlying health conditions. Could what you're eating cause your foot pain? the cause of foot pain might be closer to home than you think and may be hiding in your diet.
Yes, what you're eating could potentially cause foot pain. Certain foods can trigger inflammation, which may exacerbate conditions like gout, arthritis, and plantar fasciitis, leading to foot pain. Reducing the consumption of inflammatory foods and adopting a balanced diet can help alleviate foot pain related to dietary factors.
In this article, we'll explore the link between diet and foot pain, focusing on foods that may aggravate or alleviate this issue. We will also provide tips on modifying your diet to reduce foot pain and improve your overall health.
Provide an overview of the entire content here. We’ll talk about the following topics:
Table of Contents
What Kind of Foot Pain and Conditions Are Triggered by Foods?

Various foot pain and conditions can be triggered or exacerbated by certain foods. Here are some common foot-related issues that can be affected by dietary choices:
Plantar Fasciitis
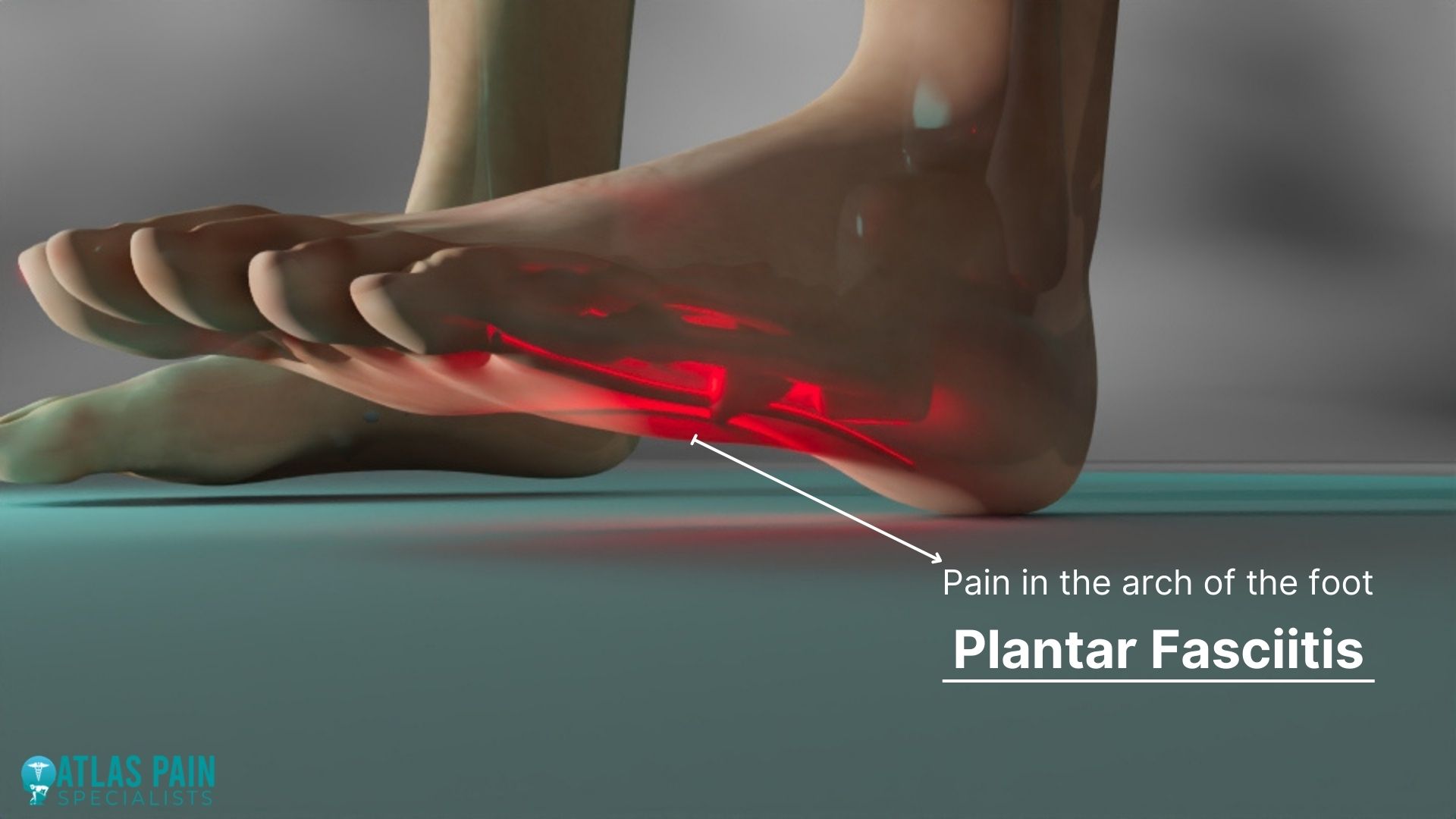
This condition is characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. Consuming excessive refined carbohydrates, sugars, and saturated fats can increase inflammation in the body, which may worsen plantar fasciitis symptoms.
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, commonly affecting the big toe. Purine-rich foods, such as red meat, organ meats, and some seafood, can increase uric acid levels in the body, which may trigger gout flare-ups.
Peripheral Neuropathy
This condition involves nerve damage in the feet, often resulting from uncontrolled diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling sensations in the feet. A refined carbohydrate and sugar diet can exacerbate peripheral neuropathy by causing blood sugar fluctuations.
Tendonitis
Inflammation of the tendons can cause foot pain and discomfort. Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats can increase inflammation in the body, potentially worsening tendonitis symptoms.
Osteoarthritis
This degenerative joint disease often affects the feet and can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Inflammatory foods like processed meats and refined carbohydrates can exacerbate osteoarthritis symptoms by increasing inflammation.
Edema
Excessive salt intake can lead to fluid retention in the body, causing swelling in the feet and ankles (edema). This swelling can worsen foot pain or make it difficult for existing conditions to heal.
You can alleviate foot pain and improve your overall health by being mindful of your dietary choices and avoiding foods that trigger inflammation or contribute to specific foot conditions.
How Do Foods Cause Foot Pain?

Foods can cause foot pain through several mechanisms, including inflammation, fluid retention, and worsening of certain medical conditions. Here are some ways in which foods may contribute to foot pain:
Inflammation
Certain foods can promote inflammation in the body, leading to foot pain. Refined carbohydrates, sugars, saturated fats, and trans fats are some examples of foods that can increase inflammation. Inflammatory foods can exacerbate foot conditions related to inflammation, such as plantar fasciitis, tendonitis, and osteoarthritis.
Fluid Retention
High salt intake can lead to fluid retention in the body, causing swelling in the feet and ankles (edema). This swelling can worsen foot pain or make it difficult for existing conditions to heal. Additionally, fluid retention can place extra pressure on the joints and soft tissues in the feet, leading to discomfort.
Uric Acid Buildup
Foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and some seafood, can increase uric acid levels in the body. High uric acid levels can lead to the formation of crystals in the joints, causing a painful type of arthritis known as gout. Gout commonly affects the big toe joint and can cause severe foot pain during flare-ups.
Blood Sugar Fluctuations
A diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugars can cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels, leading to insulin resistance and inflammation. These fluctuations can exacerbate foot pain related to peripheral neuropathy, a common complication of uncontrolled diabetes.
Circulatory Issues
Consuming excessive amounts of salt and unhealthy fats can contribute to high blood pressure and poor circulation. Poor circulation can increase the risk of developing foot problems related to peripheral artery disease and can exacerbate existing foot pain.
What Kinds of Foods Cause Foot Pain?
Several foods can contribute to foot pain by causing inflammation, fluid retention, or exacerbating certain medical conditions. Here's a list of some common culprits:
Refined Carbohydrates and Sugars
Foods high in refined carbohydrates and sugars, such as white bread, pasta, and sweets, can increase inflammation in the body, leading to foot pain. They can also cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which may worsen foot pain related to peripheral neuropathy in diabetic individuals.
Excessive Salt Intake
Consuming large amounts of salt can cause fluid retention, resulting in swollen feet and ankles. This swelling can worsen foot pain, especially in individuals with pre-existing foot conditions or injuries. Additionally, excessive salt intake can contribute to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of developing foot problems related to poor circulation.
Saturated and Trans-Fats
Foods high in saturated fats (found in fatty meats, butter, and full-fat dairy products) and trans fats (found in some processed foods like margarine and fried foods) can increase inflammation in the body. A diet rich in these fats can worsen foot pain caused by inflammatory conditions, such as tendonitis or arthritis.
Purine-Rich Foods
Purines are compounds found in certain foods like red meat, organ meats, and some seafood. When broken down in the body, purines produce uric acid, which can crystallize in the joints and cause gout, a painful type of arthritis commonly affecting the big toe. Consuming high amounts of purine-rich foods can trigger gout flare-ups and result in foot pain.
Conclusion: What You're Eating Could Cause Your Foot Pain

The link between our diet and foot pain cannot be ignored. As explored throughout this article, certain dietary choices can contribute to inflammation, poor circulation, and weight gain, all of which can exacerbate foot pain. By being mindful of our food, we can take steps to alleviate and prevent foot-related discomfort.
To support foot health, it is vital to maintain a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and certain vitamins and minerals can also help reduce inflammation and promote overall foot health. Conversely, limiting the consumption of processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can decrease the risk of developing foot pain.
In addition to dietary modifications, consulting with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored recommendations to address individual needs is crucial. A podiatrist or nutritionist can provide personalized guidance and sometimes recommend further treatment or lifestyle changes.
Ultimately, understanding the impact of our diet on foot health empowers us to make informed choices and prioritize our well-being. By adopting a holistic approach to foot care that includes proper nutrition, we can take strides toward a more comfortable, pain-free future.
About Dr. Sean Ormond



